A malware is nothing but a software with malicious intents. Technically, with a proper business model, any software can be sold as a service, then why not malware too? This brings us to the dark world of the Software as a Service (SaaS) idea, the Ransomware as a Service, or abbreviated as RaaS. Let’s get to know more about it

|
Table of Content
|
What is RaaS?
Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) is a model of business where cybercriminals create and distribute ransomware tools and infrastructure to other malicious actors for a fee. These tools and infrastructure are then used to conduct ransomware attacks by another party who is not directly connected to the creation of the malware.
By using RaaS, a person with even basic IT knowledge can launch ransomware attacks without developing the malware or handling the complex infrastructures.
How RaaS Works?
RaaS operates on a similar principle to software-as-a-service (SaaS) but with a malicious intent. In SaaS services, users are able access software applications & services remotely over the internet. Service provider develops and maintains the total infrastructure, user just pays the fee required to use the service. Usually this fee is collected in the form of subscription based fees.
RaaS operates on the same principle. Here, the developers of the software are commonly known as “operators” but can have different names like leader, developers, or system administrators as well. They are the brain behind the whole operation as they develop and maintain the ransomware software along with the associated infrastructure. RaaS developers create malware with a high chance of penetration success and a low chance of discovery.
Then, this package is offered to other less technically skilled cybercriminals who lack the brain to develop such sophisticated tools but are interested in carrying out ransomware attacks. This second party is known as affiliates. Affiliates can sign up and obtain access to the ransomware toolset. Both the operators and affiliates can perform in groups and perform cyber attacks in harmony. For a successful ransomware attack, the affiliates then payback an amount to the operators as the “service charge” thus the business continues.
In some special cases, a perpetrator group can have strong penetration testing teams but may lack the necessary ransomware software. RaaS model works as a blessing as they could just work as affiliates and use existing ransomware tools to compromise a target.
A workflow of how RaaS Model Works
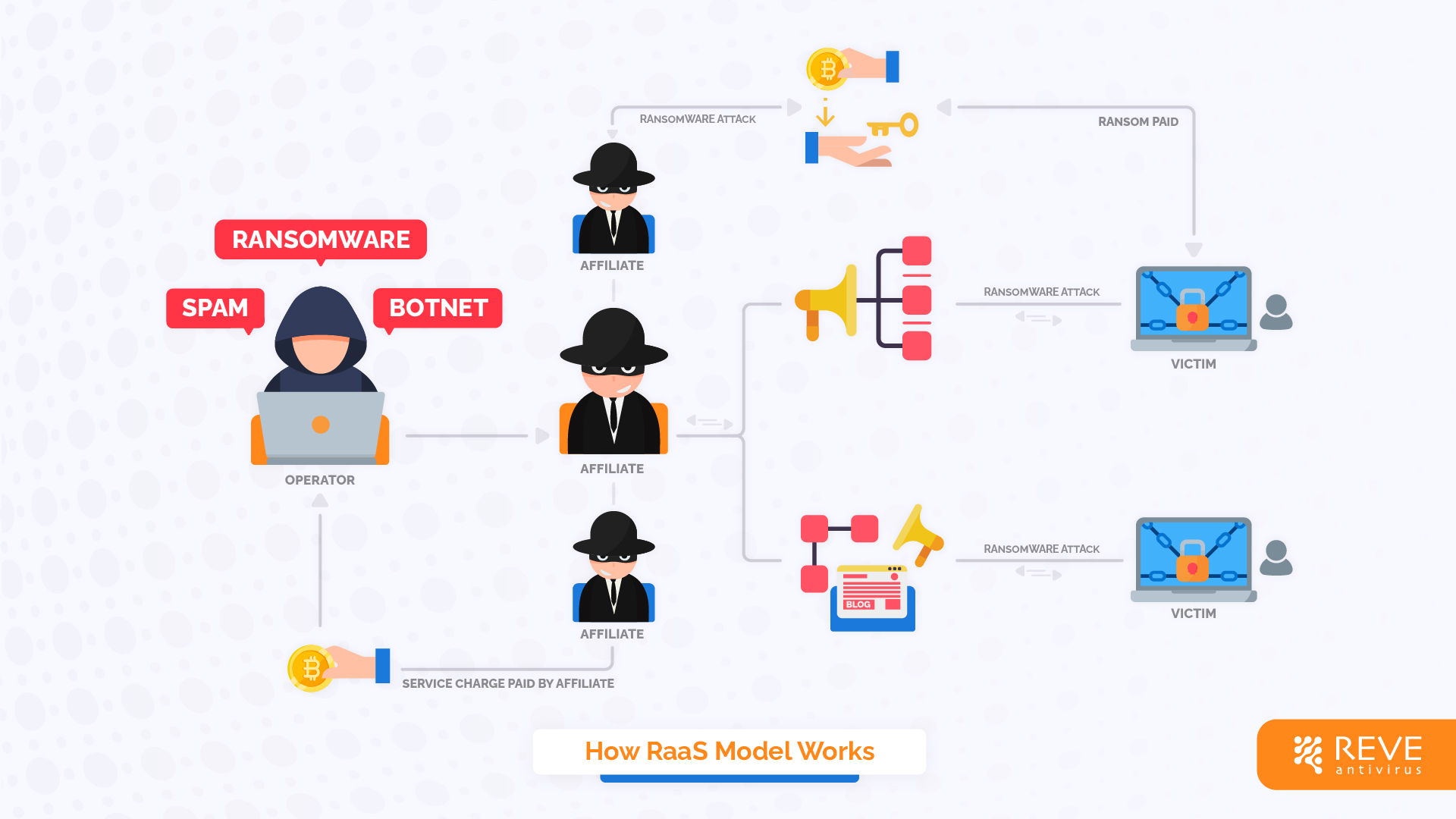
RaaS and Rise of Ransomware Attacks
As it lowers the entry barrier for cybercriminals and enables less technical individuals to participate in malicious activities, RaaS has contributed hugely to the proliferation of ransomware attacks in recent years.
By utilizing RaaS, affiliates can launch ransomware attacks without needing to develop the malware themselves or handle the complexities of infrastructure management. The operators behind RaaS platforms typically take a percentage of the ransom payments collected by the affiliates as a commission.
How to Stay Safe
Like other malicious activity, the RaaS event will probably continue to occur and has no straight-up remedy. However, the way to fight RaaS is the same as fighting with Ransomwares. Not only you need to be wary of all spam emails, phishing and other modes of a malware attack, but also the best possible cybersecurity measures around there should be implemented. All the modern antivirus or endpoint protection comes with various features like anti-spam or anti-ransomware technologies and makes your pc secure from all kinds of cyber threats.
- RaaS : The Dark Side of SaaS
- Hackers Target MOVEit Transfer’s Zero-Day Vulnerability, Emergency Patch Deployed
- How Scammers Are Utilizing ChatGPT? Few Tips To Be Safe
- World Backup Day: Why Data Backups are Important in Cybersecurity
- What is Social Engineering and How Cyber Criminals Use It
- Things To Know About Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
- What is Data Breach? Why and How It occurs? How To Prevent Data Breach


