
A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack is an attempt to make an online service unavailable by crushing it with traffic from multiple sources. DDoS Attacks target a wide variety of important resources, from banks to news websites, and present a major challenge to making sure people can publish and access important information. DDoS is already famous for the attacks on KrebsOnSecurity and DYN in 2016. This time attackers have found a new way of magnifying their attacks through Memcached Server.
In few days, a number of popular websites became victims of the DDoS attack. For example, GitHub suffered a DDoS attack, and the peak flow rate reached 1.35Tbps, according to Akamai and GitHub which is the highest DDoS attack till now.
What is Memcached
The Memcache is free and open source database-caching used to speed up the network and websites by improving the response of memory cache. This was not meant to be exposed to the internet and did not have sufficient security and hence anyone can query and get a response.
Attack Analysis
- The DDoS technique utilized as a part of this record-breaking assault mishandled common service called “Memcached” to amplify the power of their DDoS attacks. Memcached is intended to reserve information and facilitate the strain on heavier information stores, similar to circle or databases. It is normally found in cloud server situations and it is intended to be utilized on frameworks that are not specifically presented to the Internet.
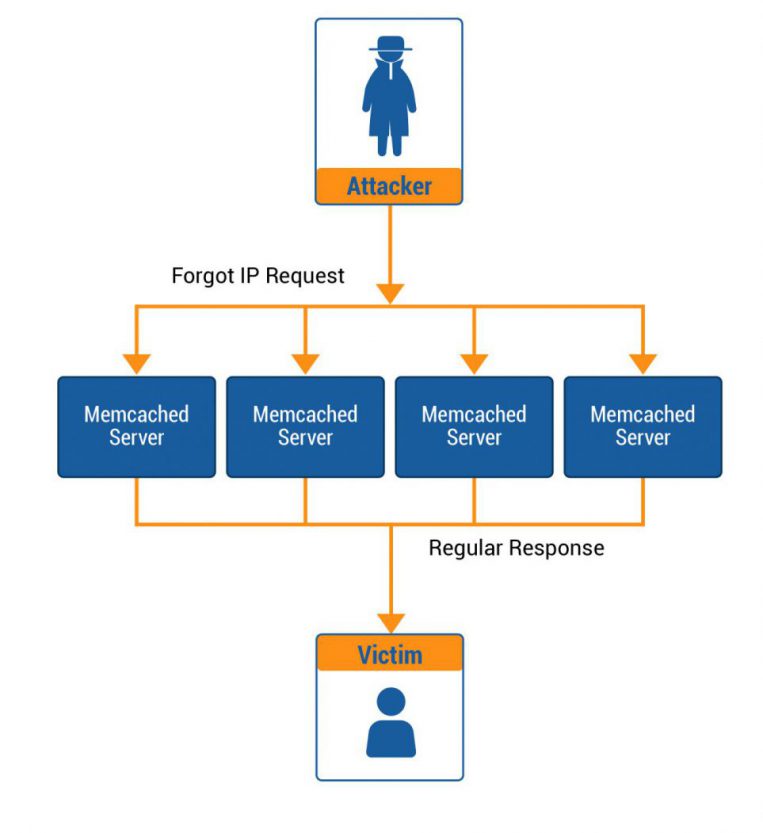
- Memcached imparts utilizing the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), which permits correspondences with no confirmation- anybody or anything can converse with it and demand information from it. Because Memcached doesn’t support authentication, the attackers are sending forged UDP protocol packets to UDP-enabled Memcached servers that are open on the internet, which in response send many more UDP packets to the target. This results in a huge amount of malicious traffic directed at the victim’s site.
- The attacker fakes his IP address into the target address and sends a request to the Memcached reflector to read the information that Memcached stored in the key-value. Memcached responds to the forged source IP upon receipt of the request, creating a reflection. When a large number of Memcached are utilized simultaneously and reply with the same forged source IP, a heavy traffic DDoS attack against this forged source IP (victim) is formed.
 Preventive Measures
Preventive Measures
- Memcached servers should be updated to version 1.5.6, released by Memcached developer’s which disables the UDP protocol by default.
- Ensure your network providers have implemented anti-spoofing so that spoofed packets used in attacks do not make it to your network.
- Proper filtering of data or usage of a binary protocol can be an effective countermeasure against these type of attacks.
- Ensure your networks have good traffic monitoring.
- RaaS : The Dark Side of SaaS
- Hackers Target MOVEit Transfer’s Zero-Day Vulnerability, Emergency Patch Deployed
- How Scammers Are Utilizing ChatGPT? Few Tips To Be Safe
- World Backup Day: Why Data Backups are Important in Cybersecurity
- What is Social Engineering and How Cyber Criminals Use It
- Things To Know About Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
- What is Data Breach? Why and How It occurs? How To Prevent Data Breach


